THANK YOU FOR SUBSCRIBING

ERP, Cloud Computing and Digital Transformation
Reinier Josias Marlissa, IT General Manager, Ateria Group


Reinier Josias Marlissa, IT General Manager, Ateria Group
What is an ERP? Well ERP is stands for Enterprise Resource Planning. ERP is a software system designed to integrate and manage various business processes within an organization. It provides a centralized platform for companies to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and enhance decision-making. ERP can be considered as complete and important integrated business system that is recommended to be implemented in every organization from small, medium up to enterprise level. ERP is also considered as an important and recommended management information system that integrates flow and process of production, planning, inventory, sales, marketing, human resources, purchasing and the last part is finance and accounting. Now let’s head back to see the history of ERP and the evolution itself, as follows
• 1960s-1980s (MRP & MRP version 2)
Material Requirement Planning or so call MRP appear in the 1960s as method to manage manufacturing process and inventory control. It is strictly focused on on calculating material requirements based on production schedules. Then in the 1980s MRP developed into Manufacturing Requirement Planning or we call it MRP version 2 and involved more functions such as capacity planning, scheduling, and financial management.
• 1990s (First ERP System)
The pronouncement of “Enterprise Resource Planning” was coined in the early 1990s to describe software systems that integrated with various organizational functions. The first ERP systems were developed by software companies like SAP, Oracle, and Baan, offering modules to manage different areas such as finance, human resources, manufacturing, and distribution.
• 1990s-2000s (Expansion and Integration)
Early 1990s are the time where a lot companies started adopting ERP systems as it gained more popularity and was also based on comprehensive benefits and features. ERP systems began to expand and started to include additional modules like customer relationship management (CRM), supply chain management (SCM), and business intelligence (BI), providing end-to-end solutions for organizations. To further enhance their capabilities, ERP systems also started integrating other technologies such as e-commerce platforms and internet. This was also the time when all ERP systems were still installed on local server (on-premises) at every server room on each organizations.
Cloud
Short brief about Cloud itself, Cloud or as we used to call, Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services over the internet on a pay-per-use basis. Instead of relying on local infrastructure and servers, cloud computing allows users to access and utilize computing resources, such as storage, processing power, and software applications, from remote data centers.
Cloud computing provides several advantages over traditional, on-premises infrastructure.
1. Cloud provides scalability and allowing organizations to easily scale up or down their computing resources based on demand. This flexibility is particularly beneficial
for businesses with fluctuating resource needs.2. Cloud computing eliminates the need for upfront infrastructure investments and reduces maintenance costs since the responsibility for managing hardware and software infrastructure lies with the cloud service provider.
Erp Can Be Considered As Complete And Important Integrated Business System That Is Recommended To Be Implemented In Every Organization From Small, Medium Up To Enterprise Level
3. It enables remote access to data and applications, facilitating collaboration and mobility.
4. It also provides us with instituted multiple redundancies to make sure that if something went bad then we still had a backup as a part of disaster recovery plan and can be reactivated within hours or even minutes.
For Cloud computing services, there are 3 (Three) types of services:
1. IaaS : Infrastructure as a Service
2. PaaS : Platform as a Service
3. SaaS : Software as a Service
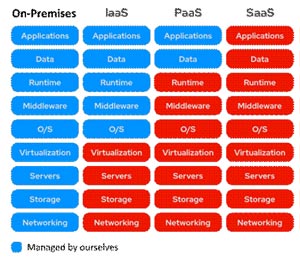
The table below is of the type of models, the benefits, and how we can use any or all of them to create a cloudcomputing environment that meets all of our needs. With this table you will get clear understanding on how Cloud computing management between all Cloud computing services compare with, on-premises model.
How is ERP and Cloud Related?
With the advancement of cloud computing technology, ERP systems began shifting to cloud-based models, offering greater scalability, flexibility, and accessibility. Starting from 2010s to present, there has been a significant shift towards cloud-based ERP systems, often referred to as ERP in the cloud or cloud ERP.
Cloud-based ERP solutions offer several advantages over traditional on-premises ERP systems, including:
• Lower upfront costs: Cloud ERP eliminates the need for extensive hardware investments and reduces upfront software licensing costs.
• Scalability: Cloud ERP systems can easily scale up or down based on the organization's needs, allowing for flexibility and accommodating business growth.
• Accessibility: Cloud ERP enables users to access the system and data from anywhere, promoting remote work, collaboration, and mobility.
• Automatic updates: Cloud ERP providers handle system updates and maintenance, ensuring that users are always on the latest version without any manual effort.
• Data security and backup: Cloud ERP providers typically have robust security measures and backup systems in place to protect data from loss or unauthorized access.
• Integration and interoperability: Cloud ERP can seamlessly integrate with other cloud-based systems or third-party applications, facilitating data exchange and interoperability.
The rise of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) providers, such as Oracle NetSuite, Infor Cloudsuite, Microsoft Dynamics, SAP Hana and others ERP products brand offered ERP functionality through subscription-based models, making it more affordable for small and mediumsized businesses.
Overall, cloud computing has revolutionized the ERP landscape by providing organizations with a more flexible, cost-effective, and accessible approach to managing their operations and resources.
Cloud ERP and Digital Transformation
Cloud ERP systems are a key enabler of digital transformation initiatives. They provide a solid foundation for organizations to integrate various digital technologies, streamline operations, and enable data-driven decisionmaking. ERP systems serve as a centralized hub that connects different functions, processes, and data sources, facilitating the flow of information required for digital transformation.
By implementing a cloud ERP system, organizations can enhance their ability to leverage emerging technologies, drive innovation, and achieve their digital transformation goals.
Nowadays, cloud ERP systems have evolved to support digital transformation initiatives. They now incorporate emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), Internet of Things (IoT), and data analytics.
In summary, cloud ERP systems play a vital role in supporting digital transformation efforts by providing a unified platform for managing core business processes and enabling integration with other digital technologies. Together, ERP, cloud and digital transformation can help organizations enhance their competitiveness, improve operational efficiency, and deliver better experiences to customers.












